Electric Field
Electric Field: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Electric Field, Inverse Square Law, Electric and Gravitational Field, Electric Field Due to a Point Charge, Electric Field Due to Two or More Charges, Electric Field at a Point in Vector Form, etc.
Important Questions on Electric Field
A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges Q. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if
Assertion: Due to two point charges electric field and electric potential cannot be zero at some point simultaneously.
Reason: Field is a vector quantity and potential is a scalar quantity.
Two point charges and are placed some distance apart. If the electric field at the location of be , then that at the location of will be
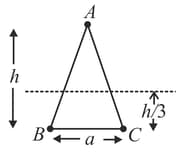
Two equal positive charges are placed at the vertices and of an isosceles triangle of base and height , as shown in the adjacent figure. When a charge is placed at it is found that at a point inside the triangle, the net electric field due to the three charges vanishes. If this point is at a height then what is ?
The maximum field intensity on the axis of a uniformly charged ring of charge and radius will be
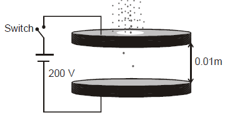
Two large circular discs separated by a distance of are connected to a battery via a switch as shown in the figure. Charged oil drops of density are released through a tiny hole at the center of the top disc. Once some oil drops achieve terminal velocity, the switch is closed to apply a voltage of across the discs. As a result, an oil drop of radius stops moving vertically and floats between the discs. The number of electrons present in this oil drop is ______.(neglect the buoyancy force, take acceleration due to gravity and charge on an electron )
Infinite number of charges of magnitude each are lying at metre on -axis. The value of electric field intensity at point due to these charges will be , find the value of ,
In Millikan's experiment, static electric charge on the oil drops has been obtained by shining -rays. If the static electric charge on the oil drop is , calculate the number of electrons present on it.
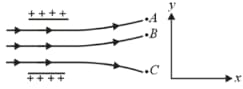
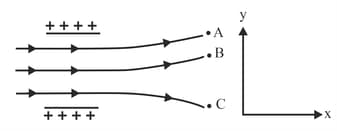
The tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field are shown in the figure. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio?
If the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is zero then
A metal plates of capacitor of area carries a charge of . Calculate the outward pull on plate (in newton).
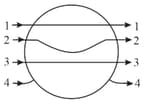
A metallic shpere is placed in a uniform electric field. The line of force follow the path(s) shown in the figure as,
The maximum field intensity on the axis of a uniformly charged ring of charge and radius will be
A thin conducting ring of radius is given a charge . The electric field at the centre of the ring due to the charge on the part of the ring is . The electric field at the centre due to the charge on the part of the ring is
The tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field are shown in the figure. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio?
If the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is zero
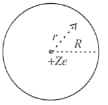
An early model of an atom considered it to have a positively charged point nucleus of charge surrounded by a uniform density of negative charge upto a radius . The atom as a whole is neutral. The electric field at a distance from the nucleus is
Force acting upon a charged particle kept between the plates of a charged condenser is . If one of the plates of the condenser is removed, force acting on the same particle becomes